Ebaas Platform Backend Services
Ebaas backend services is a set of RESTful web services that help you build your business applications faster with greater ease. Instead of worrying about REST API code semantics and dealing with backend business logic and database operations, you can focus on developing the web or mobile front-end that delivers a good user experience.
In this post, Each backend service is quickly introduced below. If you are interested in learning more about the backend service APIs, you can download and install Ebaas platform. Then, start the Server, open web browser to view the API’s online documentation (See Fig. 1) at http://localhost:8080/swagger
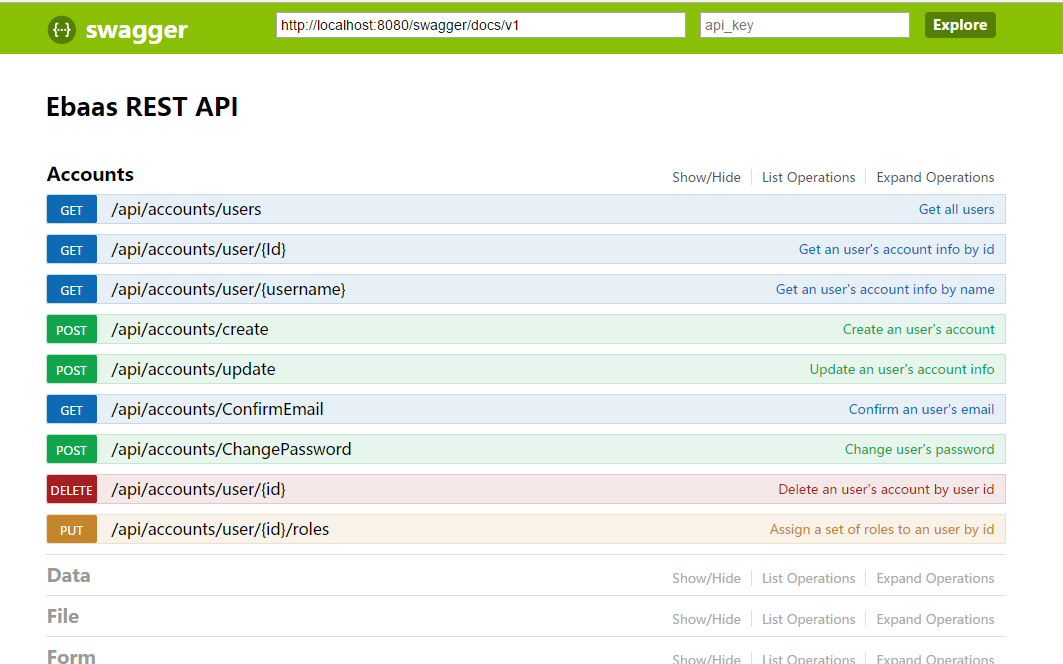 Fig.1: Online Documentation of Backend Services
Fig.1: Online Documentation of Backend Services
The online document interface allows you to run APIs of the backend services (See Fig. 2).
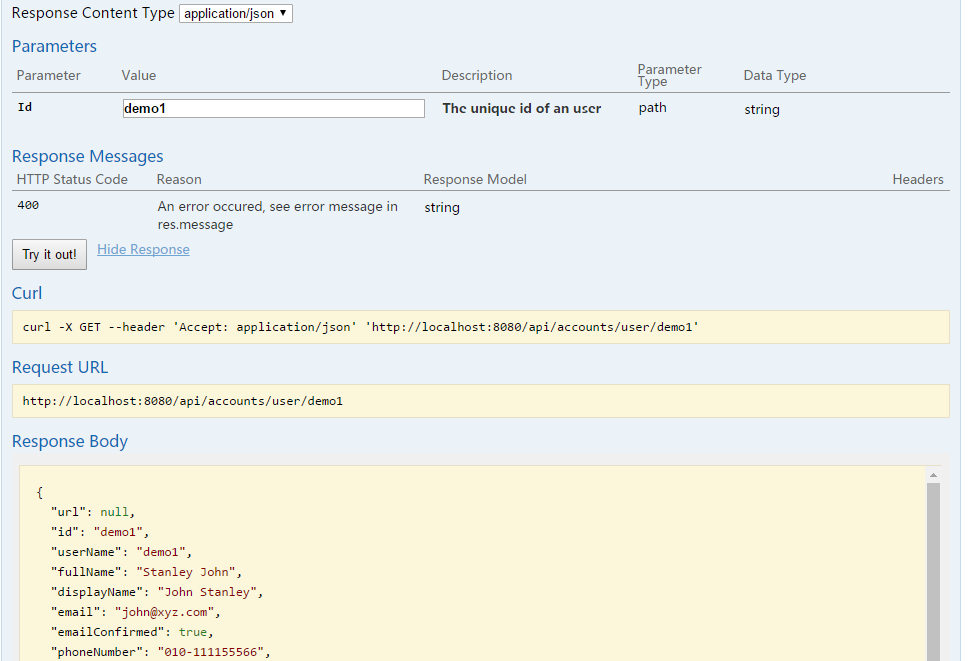 Fig.2: Try API online
Fig.2: Try API online
Introduction of the Backend Services
Accounts Service
The Accounts Service allows you to manage user accounts and roles in your application. It has a set of APIS operations for reading, creating, updating, deleting users or roles and assigning roles to users.
Data Service
The Data Service is a model-driven web service. You can use the APIs of the service to perform CRUD operations on any of the classes in your application data model without coding. The service stores the data in a relational database, such as SQL Server or Oracle.
Time Series Service
The Time Series Service is a particular web service that has a set of operations of reading time series data from files, forecasting time series based on a machine learning model, and publishing predictive machine learning models.
Forms Service
The Forms Service is a model-driven web service. It supports creating dynamic forms using data model and templates. It allows you to offer various forms in your business application with coding.
Files Service
The Files Service stores files that your application needs to store on a file server. It has set of operations for uploading, downloading, and deleting files associated with a data instance.
Image Service
The Image Service stores image files that your application needs to display. It has set of operations for reading, uploading, and deleting images.
Tasks Service
The Tasks Service allows you to manage workflow tasks so that your application can support business processes.
Message Service
Using the Message Service for sending push notifications to your applications removes the complexity of integrating with multiple vendor-specific notification services and gives you an easy to use push portal.
Metadata Service
The Metadata Service has a set of operations of getting metadata in JSON formats. It allows you to develop metadata-driven user interface components that are adaptive and customizable.
ImportExport Service
The ImportExport service allows you to import data from files using a canned import process and export a set of data as a data package.
Reporting Service
You can use the Reporting Service to generate a report using a template and download it in Word or Excel format.
SiteMap Service
The SiteMap Service allows you to develop a framework of your frontend driven by a sitemap model so that users with different roles can have personalized user interface.
Kanban Service
Kanban is Japanese for “visual signal” or “card.” The Kanban’s highly visual nature allowed teams to communicate more easily on what work needed to be done and when. The Kanban service allows you to build a Kanban user interface component.
Log Service
The Log Service provides the APIs for getting logging information about actions performed on the data.
Getting Started with the Backend Services
The Backend Services RESTful API provides a universal way of using the Backend Services components of Ebaas from any platform that can send HTTP or HTTPS requests. It exposes the complete set of APIs available to the app developer.
Usage
To use the Backend Services, you need to be able to send HTTP or HTTPS requests. Use your favorite library, such as Angular or React, to make RESTful calls from your app code. The general structure of calling URL is as follows:
http://host:port/api/{service-name}/{resource}
where
- http://host:port/api is the base URL to which you send all requests
- {service-name} is the name of a backend service, such as accounts, data, form, etc.
- {resource} is a path containing one or more identifiers of resources that you want to work with
Most operations need an authorization using a token which is returned from the authentication API. You need to include the token in the header of each request you send. Examples:
http://host:port/api/accounts/user/demo1 http://host:port/api/data/TDM/Issues http://host:port/api/data/TDM/Issues/29302911
HTTP Verbs
Using different HTTP verbs with the same URL yields different results. For example, using the GET verb with http://host:port/api/data/TDM/Issues reads all issue instances; using the POST verb creates a new issue instance provided the required data as an HTTP body.
Error Codes
When you request a RESTful API operation that cannot be executed by Ebaas Server, you get an error code in response to let you know where the problem lays. Some of these error codes are mapped to standard HTTP status codes. See the online document to learn more about what each error code means and when it is returned.